Search K
Appearance
Appearance
This guide explains how to configure and use the Loop node in your automation workflows to process collections of items one at a time, running a sub‑workflow for each.
| Input Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Array Object | text | An expression that evaluates to a list/array. Use placeholders ({...}) to reference workflow data. |
| Count | number | (Alternative) An integer N. If provided and Array Object is empty, the loop runs N times (items 1 to N). |
Note: Exactly one of Array Object or Count must be set.
The Loop node itself writes these into task data, making them available to downstream tasks:
Next (case‑insensitive). This child will be cloned and run for each item.Completed, specific status names, or switch outputs).Finished (case‑insensitive).[Loop]
└─ (Next) → [FirstTask] → [SecondTask] → ...
└─ (Finished) → [CleanupTask]Initialization: Evaluate Array Object or Count and store items as LoopItems.
Iteration Loop:
For i from 0 to IterationCount - 1:
Clone the Next child task, stamp LoopItem = LoopItems[i] and IterationIndex = i.
Execute its entire subgraph synchronously:
Default if a switch or if‑node is used.AndOperator joins: waits until all upstream tasks complete before executing.When the subgraph ends, move to the next iteration.
Finished branch: if defined, run its tasks once after all iterations.
Apple, Banana, Default). The engine picks the branch whose route name ends with the task’s statusReturn value (case-insensitive). Fallback to Default if no exact match.taskSuccess = false will cancel the entire workflow.QueueWorkflow completes, the workflow stops with status Accepted (202) and triggers a new workflow.DataReturnObject completes, the workflow stops immediately, returns its ReturnData via the API (status 200), and does not continue looping.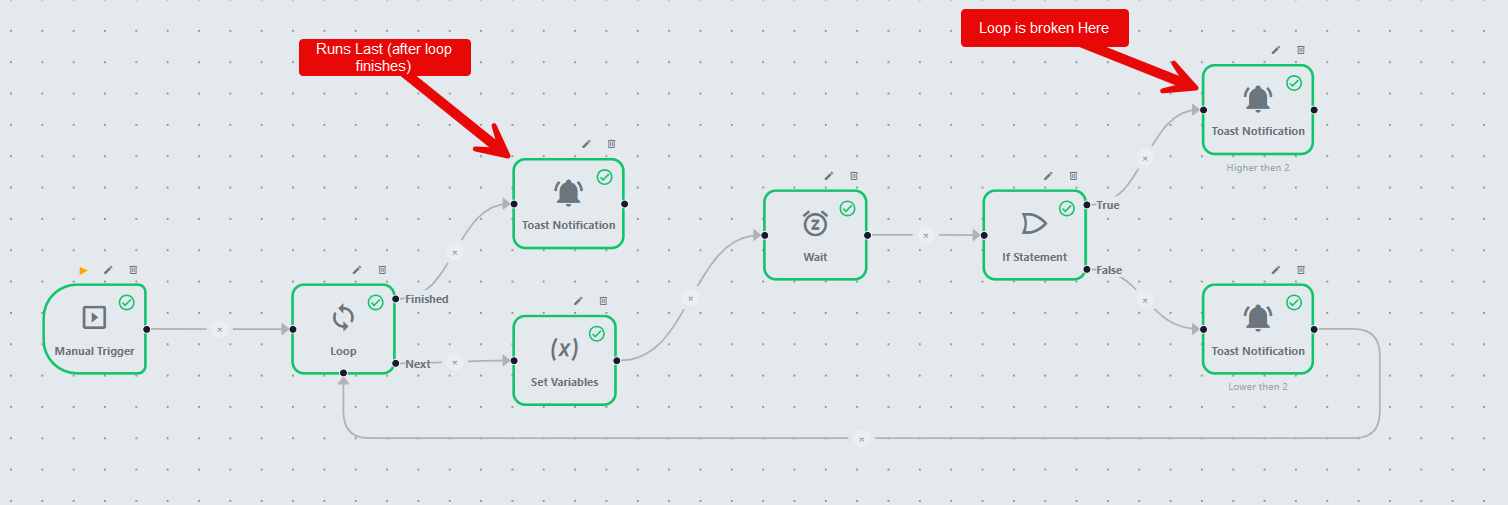
Array Object expression yields a non-empty list or provide a valid Count.Next/Finished branches).For more details or support, visit our Knowledge Base or contact the Automation team. Happy looping!